Torque sensors: removal, disassembly, and calibration

The improper operation or failure of an electric steering rack does not necessarily require the unit replacement. The rack can be repaired, provided the shop has special equipment fit for the task. A lot of steering rack faults result from the failure of various torque sensors. For example, a specific design of torque sensors of steering racks in Subaru, Honda, or Mazda often becomes the cause of the malfunction.
The symptoms can be as follows:
- turning a steering wheel to the right and to the left requires different applied efforts
- self-twisting of the steering wheel all the way to one side when starting the engine
When this sort of trouble happens, restoration of the steering rack function requires removal and disassembly of the torque sensor. If nothing else except for the signs of wear has been found during the examination, the torque sensor can be re-assembled, installed back on the steering rack, and calibrated. Replacement of the sensor is necessary in case of mechanical breakdown. The new one should be calibrated as well.
When the steering rack is connected to controllerMS561 via adapterMS550, we can view the current value(s) of the torque sensor. Depended on the torque sensor design, there can be one or two displayed voltage values. If there is only one value (Fig.1), calibrating the sensor would mean adjusting this value proximal to zero.
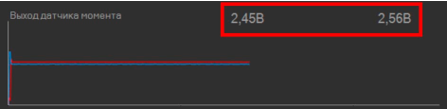
Fig.1
In case there are two displayed values (Fig.2), they should be adjusted to make two close values.

Fig.2
The calibration can be performed by either changing the position of the sensor body or setting the potentiometers on the sensor board.
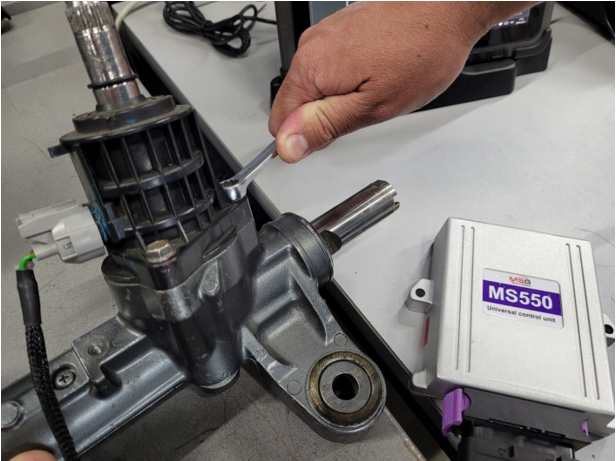

Fig.3
In such a way, using controller MS561 and adapter MS550, we can restore the steering rack function. Now we can check the unit and assess the quality of the performed work.








